What can functional connectivity tell us about cognition and behaviour?
Objective
- Describe different approaches to studying human functional connectivity
- Outline the organisation of the brain into intrinsic connectivity networks,
and their relationship to cognition - Provide examples of methods to study links between functional connectivity and behaviour & cognition
Functional connectivity construction:
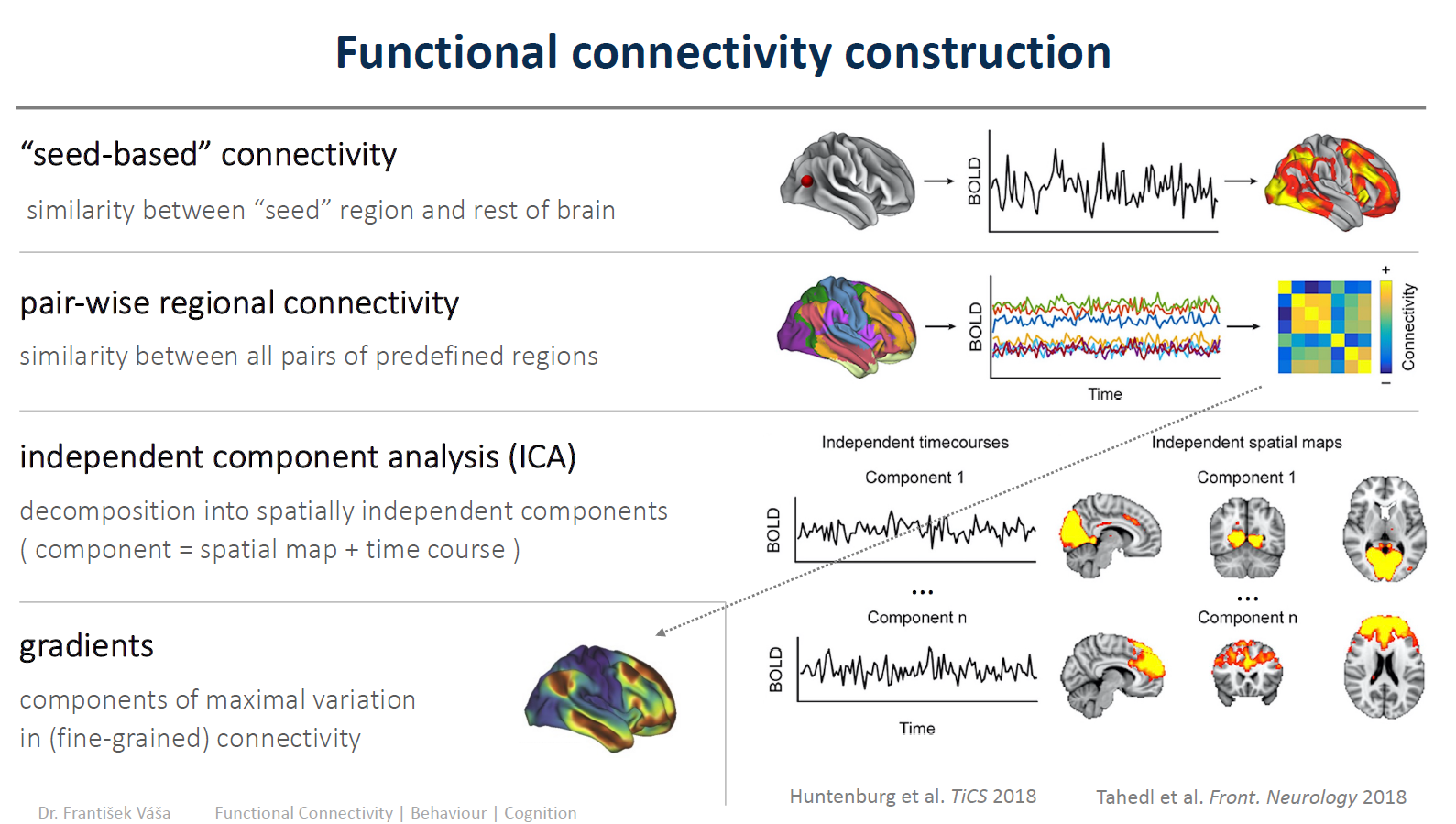
Options in functional connectivity construction:

Functional (MRI) data pitfalls: head motion (& other artefacts)
Data base for meta-analyses of fMRI data: neurosynth.org; brainmap.org
Summary
Frontier of brain imaging
Myelin mapping using mcDESPOT
3D motion correction -PROMO
Looping star (Wiesinger rt al. 2018 MRM): silent
Baby in Uterus
MAttia Veronese - ^18^F-DOPA PET imaging: Brain Chemistry
Fernando Zelaya - Perfusion MR imaging: Brain Physiology Quantitative whole brain imaging of cerebral blood flow
Informing treatment development in ADHD
Existing treatment: Methylphenidate
Potential new medication: Atomoxetine
[Portable MR][https://www.kcl.ac.uk/news/europes-first-game-changing-portable-mri-machine-arrives-at-kings-health-partners]
Adam Hampshire the Great British Intelligence Test 2020
Imbalance in catecholaminergic functional circuits might underlie cognitive fatigue in multiple sclerosis
Cognitive neuroscience of cognitive control
Cognitive control functions
- Motor response inhibition: the ability to inhibit a prepotent motor response
- Go/no-go task
- Stop task
- Interfere nee inhibition: the ability to inhibit a prepotent tendency to respond to an
interfering stimulus/overriding a conflicting motor response- Simon task
- Eriksen Flanker task
- Colour-Word Stroop task
- Cognitive flexibility: the ability to inhibit a response that is no longer appropriate &
reengage 1n a new response- Wisconsin Card Sorting task
- Other switching tasks; STOP-Change task
TDCS is cheaper than TMS
Overall conclusions
- Lateral & medial fronto-striatal areas mediate cognitive control
- R IFG, pre-SMA, caudate, subthal. nucleus for motor inhibition
- R & L IFG, caudate, ACC for interference inhibition
- R & L DLPFC/IFG, R & L IPL, basal ganglia for switching
- Anterior insula is crucial for saliency processing
- There is progressive increase in activation of areas that mediate development (not sure)
- these functions from childhood to adulthood
- R IFG, SMA, caudate, subthalamic nucleus for inhibition
- R & L IFG, caudate, ACC for interference inhibition
- L & R IFG, L & R IPL, basal ganglia for switching
- ADHD patients have functional deficits in these areas
- R IFG/ AI, SMA/ ACC, caudate, thal for motor/interference inh.
- R & L IFG, basal ganglia for switching
- =>likely a delay of neurofunctional maturation?
Vocabulary
IFG: inferior frontal gyrus
AG: angular gyrus (PL)
MFG: medial frontal gyrus (DLPFC)


