Experimental design
categorical design
distinct types of stimuli or the timing, participant instructions
factorial design
usually 2 pairs of controlled factors
parametric design
modify the control variables
Timing of stimuli
block design
Block some variables
pros
most commonly used
statistically the most powerful
cons
can be predicable, lead to rapid habituation or anticipation (reduced response)
cannot extract specific stimulus brain response
some design cannot be modelled as a block
can be affected by cumulative effects (context)
event-related design
Each stimulus is individual epoch (can be associated with discrete events)
pros
parallel behavioural studies
greater flexibility (more complex)
cons
related designs require a greater understanding of fMRI because the design (more complex)
less statistical power (can be reduced to extend the scanning time)
mixed design
mix the two above design together
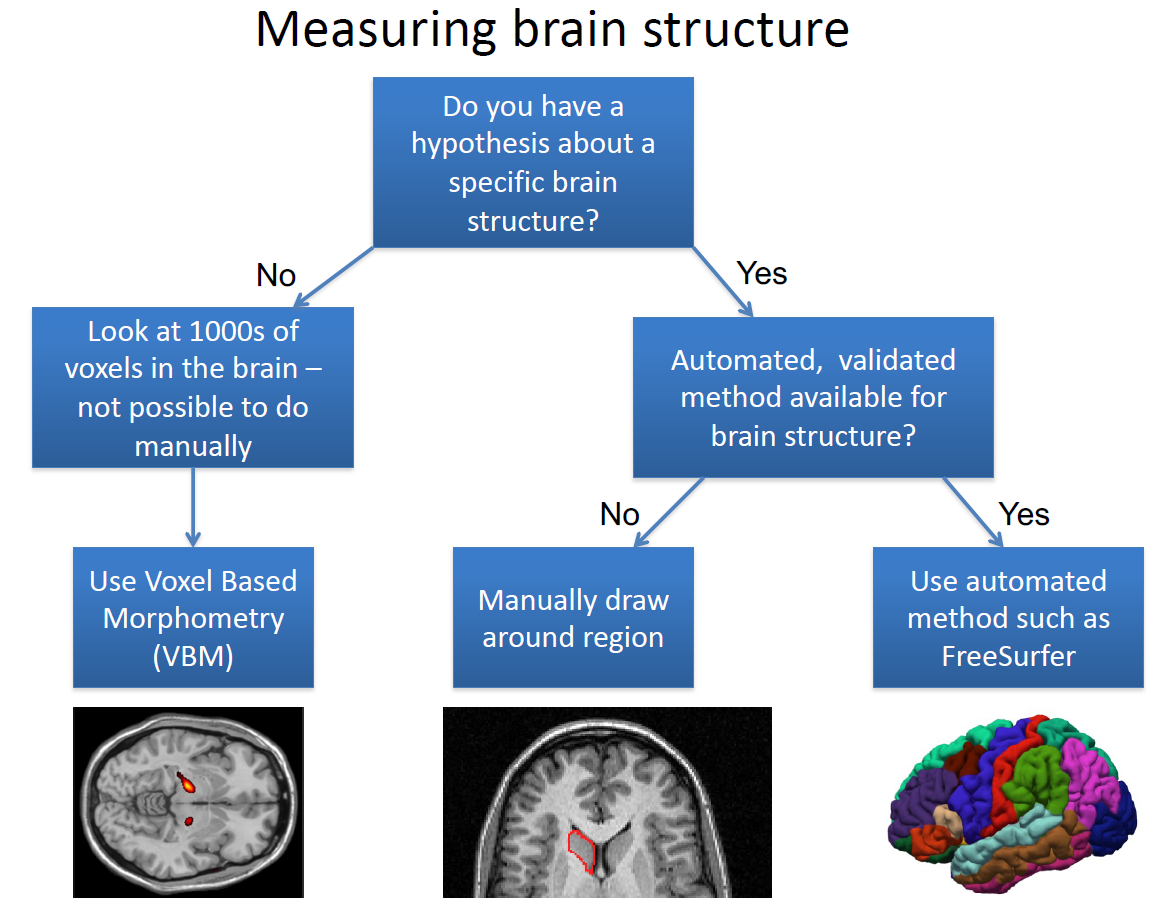
Structural MRI: Focus on analysis with Voxel Based Morphometry (VBM)
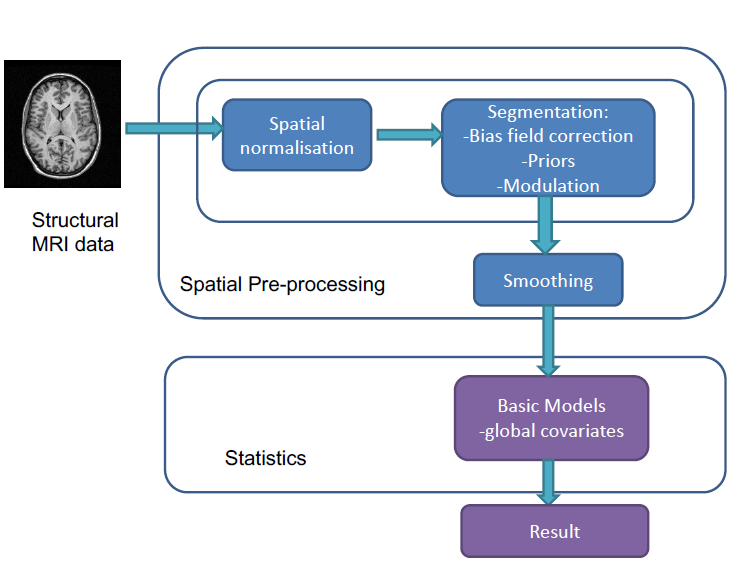
Spatial Normalization
transform a brain image into a standard brain coordinate system
SPM (Statistical Parametric Mapping) spatial normalisation
Segmentation
We do not use intensity threshold to segment for the following reasons:
User intervention to decide what lever to threshold
Bias field correction (an MRI artefact which causes slow changes in image intensity across the brain)
Image noise (random regions of white matter have low levels of intensity which may be classified as grey matter)
Modulation can increase the contrast ratio (an analogy: just like the reverse of using a rolling pin on pastry)
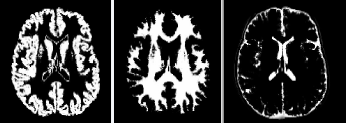
Normalised:
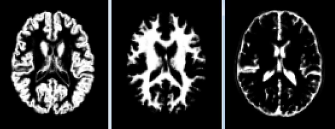
Modulated:
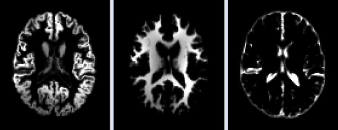
(form left to right: Grey, White and CSF (Cerebrospinal fluid))
Smoothing
Take into account variations in structural anatomy
To reduce noise
To increase the normality of the data
Smoothing amount is measured as FWHM (A common smoothing kernel for VBM is 8-12mm)


