review basic concepts about neuronal activity
Two ways to propagate information: 1. electrical potential; 2. chemical neurotransmitters
Generation of signals (both) only require kinetic energy already available
discuss the mechanisms that lead to spontaneous electrical activity in neurons
discuss basic concepts about neuro-transmitter function
Restoration of electro-chemical potential requires a huge amount of additional energy that can only be met by increases in metabolism
Reuptake and recycling requires a lot of additional energy from increases in metabolism
discuss the energy requirements for neuronal and synaptic activity
There are only a small amount of glycogen in brain so that a vast supply of oxygen and glucose delivered by a highly specialized vascular network is necessary
discuss the control of blood flow in brain tissue and its relevance
Increases in neuronal activity are always accompanied by a local increase in regional Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF)
Understand the physical principles of Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) contrast
Paramagnetic deoxyhemoglobin in venous blood is a naturally occurring contrast agent (Ogawa, 1990)
The BOLD contrast depends on the relationship between three processes:
(b) the magnetic properties of the haemoglobin in the blood
(a) the increase in blood flow triggered by the increase in cellular activity
(c) the mismatch between the increase in blood flow and the increase in oxygen metabolism
BOLD contrast depends on the relationship between CBF (Cerebral Blood Flow) and CMRO2 (Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen)
increases in CBF, CMR
glucand CMRO2comes as a result of increases in neuronal activityHowever, paradoxically: the oxygen extraction fraction (E) (E = (oxygen consumed) / (oxygen delivered)) DECREASES with INCREASES in neuronal activity.
Increased neuronal activity leads to a DECREASE in the concentration of de-oxyhaemoglobin in venous space
Why does this reactive hyperemia occur? One explanation is to transport oxygenated haemoglobin
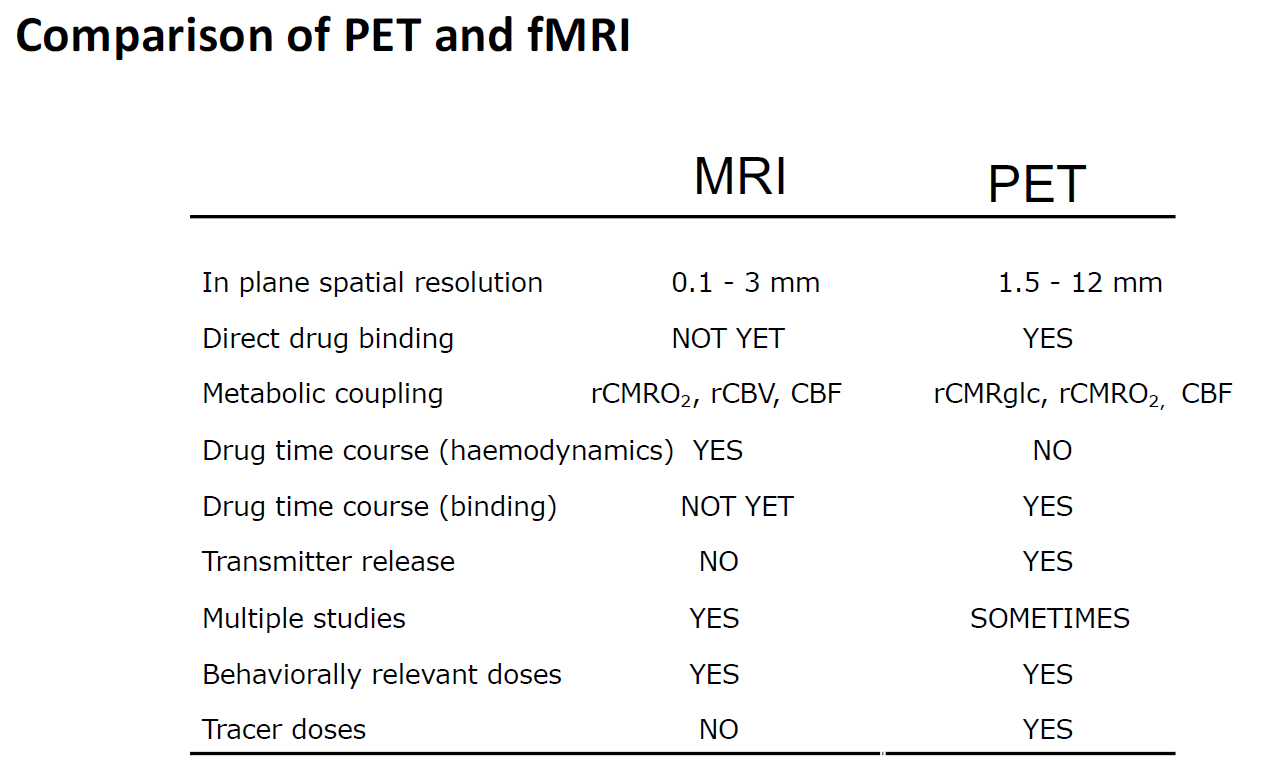
• Understand the basic methods used to assess drug effects with MRI
• Appreciate the utility of phMRI
• Understand the key differences in PET and MRI for drug effects
PET is much more expensive even though MRI is expensive
• To be able to identify major confounds
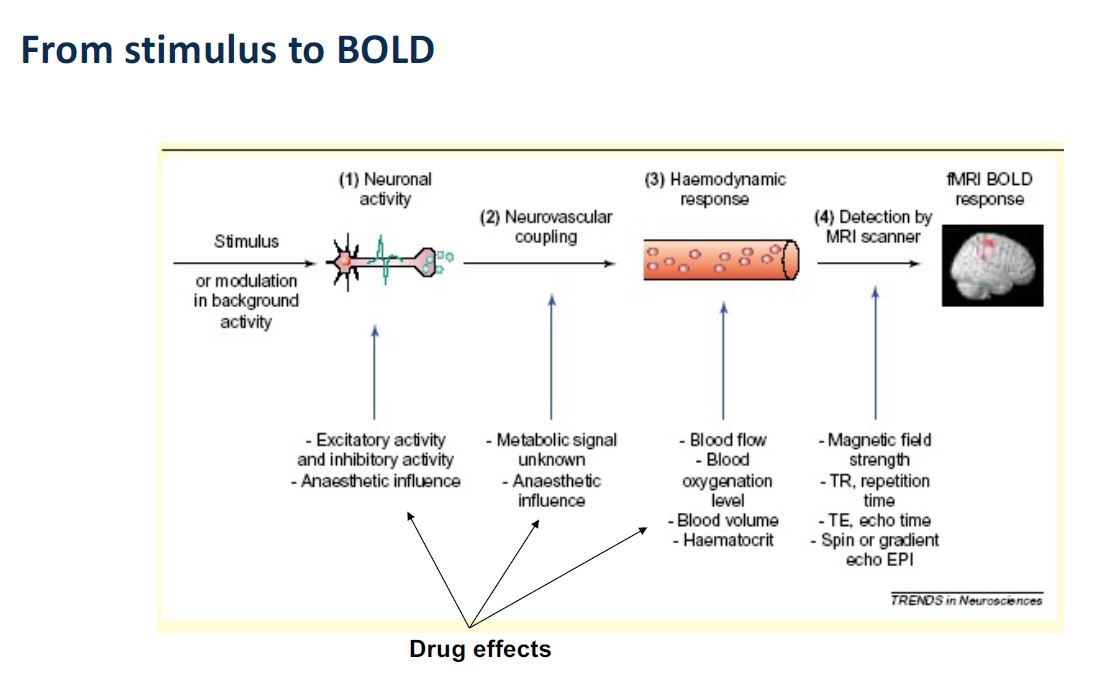
• To be able to describe solutions to confounds
We may meet some problems with building and using BOLD predictors
- The BOLD response is delayed, has dispersed/wide and variable shape
- BOLD signals include substantial amount of low-frequency noise


