the angular momentum denoted as I and can be 1/2, 1, 3/2 …
The frequency of precession (the frequency of our signals) is
governed by the ‘Larmor’ formula
𝜔 = 𝛾 𝐵
where:
ω: is the Larmor frequency of precession
γ: is gyromagnetic ratio
(a constant for each nucleus)
B: is the amplitude of the magnetic field
Q: homogeneous magnetic field does not exist. How do we eliminate this detection error?
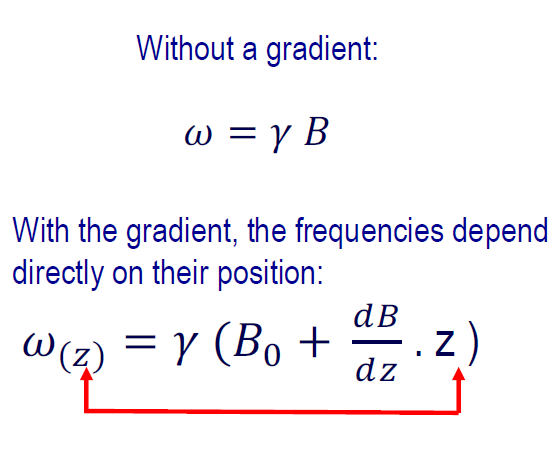
A: in a small zone.
the MRI data acquires information from the inverse domain of the object, organ, patient, etc. It is called ‘k-space’
Learning objectives (part I):
• Understand the phenomenon of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and how we detect NMR signals
The nucleus of a stuff as a whole has angular monument. Under a magnetic field, they behave as magnets, experience precession (A comparatively slow rotation of axis of rotation of a spinning body about a line intersecting the spin axis. The smooth, slow circling is precession, whereas the uneven wobbling is nutation. The frequency is given by ‘Larmor’ formula 𝜔 = 𝛾 𝐵).
We detect NMR signals with resonance. The spins will absorb the energy (radio-frequency waves) with an equal frequency to precession (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance). When we stop giving the energy, the nuclei will emit the energy. Thus we can detect. However, the direct detection is impossible because of the main external field. The trick is to rotate net nuclear magnetization with a small perpendicular magnetic field (oscillating at 𝜔, i.e. on resonance). Then we turn it off when magnetization rotate by 90deg. During the rotating-back stage, a current will be induced in our induction coil enabling us to detect.
• Understand what is a magnetic field gradient
• Understand how Magnetic Field Gradients can be used to make Magnetic Resonance signals dependent on position
• Understand how this process is used to generate images
fMRI and structural images are often 16-bit
| 8 bit | char |
|---|---|
| 16 bit | short |
| 32 bit | float |
NifTI is the standard format for MR image (,nii)
There are three applications of image registration
Head-motion correction (aka realignment): keep all images the same shape and size, we only want to move it (translations) or rotate it (rotations)- This is termed “Rigid Body Registration”
For distinct participants, Co-registration is necessary,
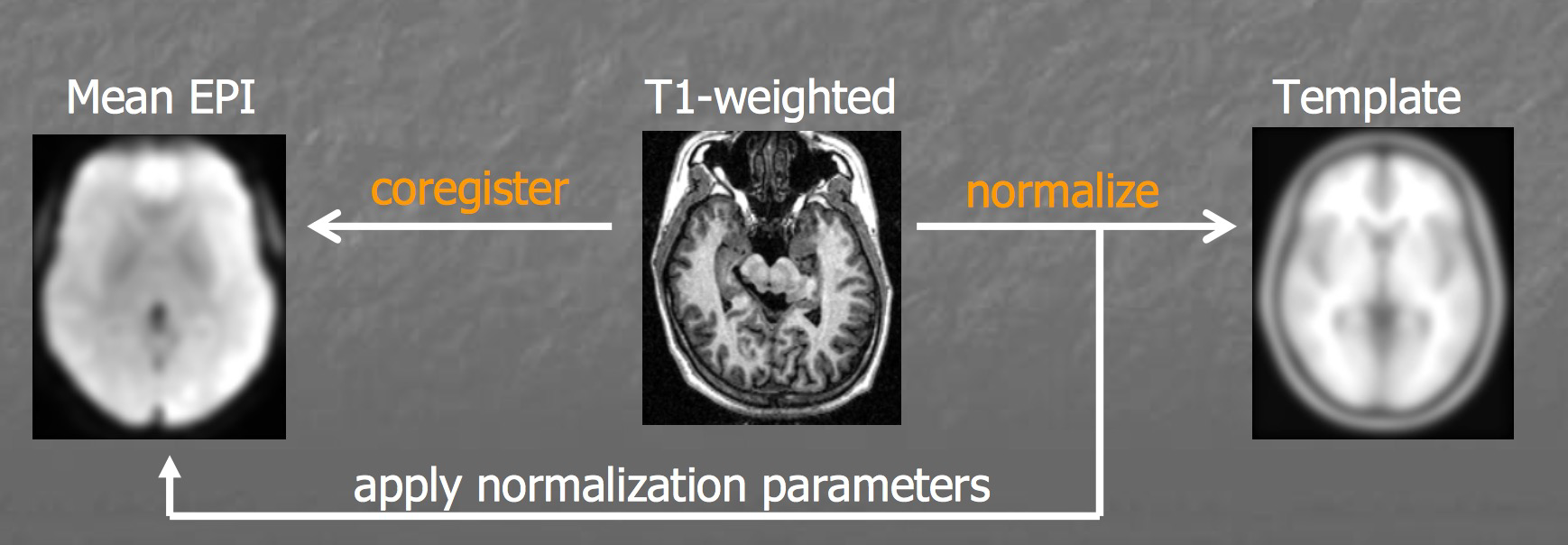
- Another approach is normalization.
- Affine transformations
- Non-linear wraps


